NeuralLabeling: A versatile toolset for labeling vision datasets using Neural Radiance Fields
2: Tohoku University
Under review
Abstract
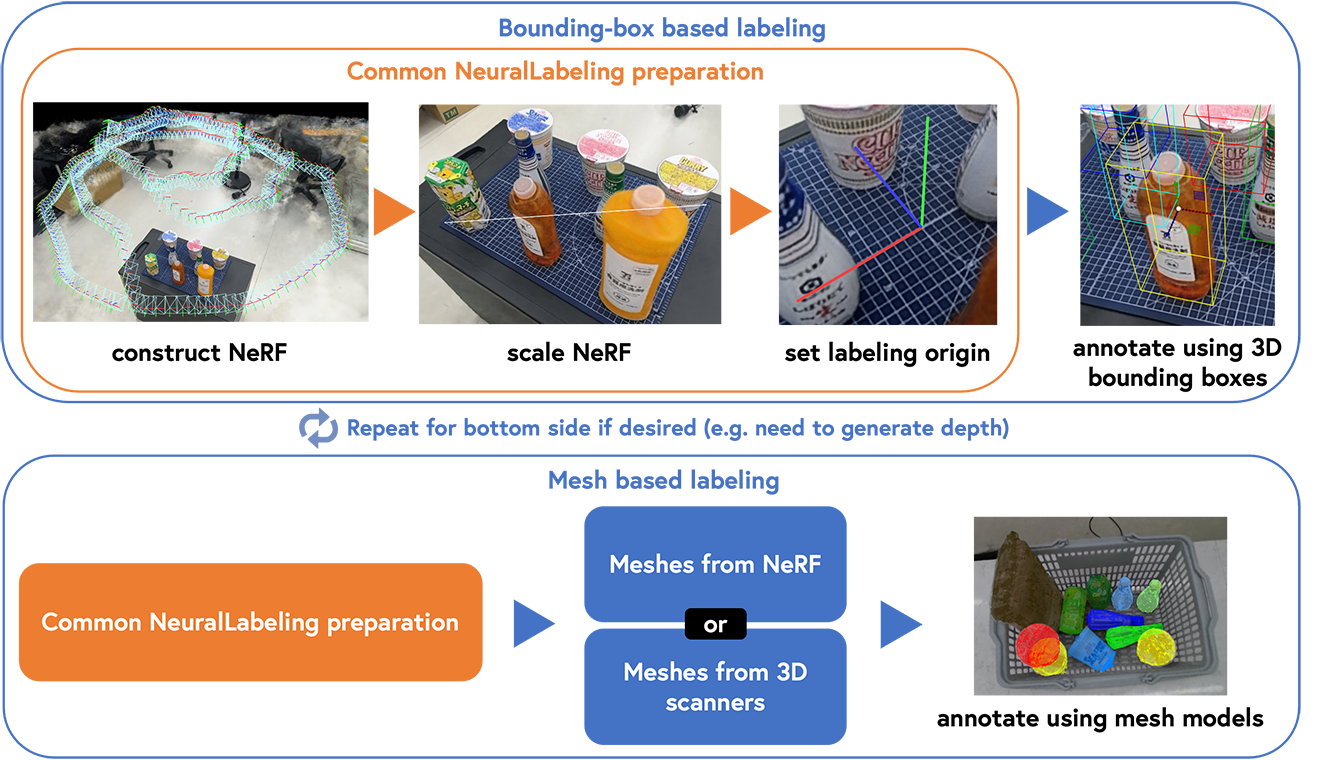
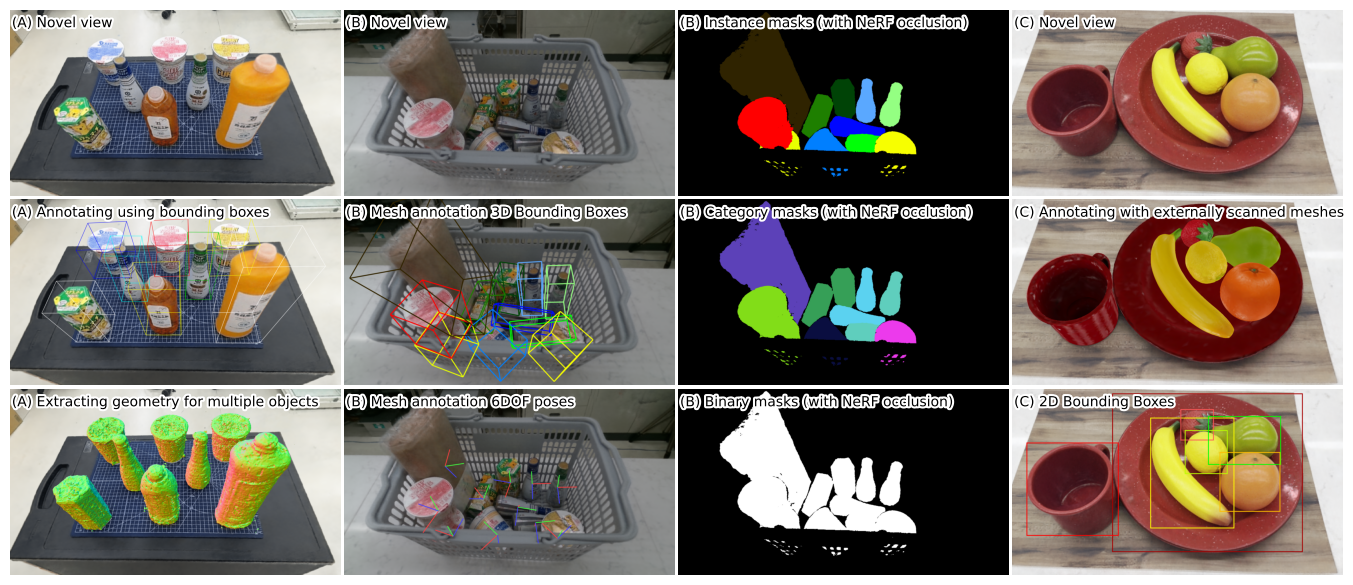
We present NeuralLabeling, a labeling approach and toolset for annotating a scene using either bounding boxes or meshes and generating segmentation masks, affordance maps, 2D bounding boxes, 3D bounding boxes, 6DOF object poses, depth maps and object meshes. NeuralLabeling uses Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) as renderer, allowing labeling to be performed using 3D spatial tools while incorporating geometric clues such as occlusions, relying only on images captured from multiple viewpoints as input. To demonstrate the applicability of NeuralLabeling to a practical problem in robotics, we added ground truth depth maps to 30000 frames of transparent object RGB and noisy depth maps of glasses placed in a dishwasher captured using an RGBD sensor, yielding the Dishwasher30k dataset. We show that training a simple deep neural network with supervision using the annotated depth maps yields a higher reconstruction performance than training with the previously applied weakly supervised approach.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JST [Moonshot R&D][Grant Number JPMJMS2031]. This research is subsidized by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) under a project JPNP20016. This paper is one of the achievements of joint research with and is jointly owned copyrighted material of ROBOT Industrial Basic Technology Collaborative Innovation Partnership.
Method
Demonstration of outputs
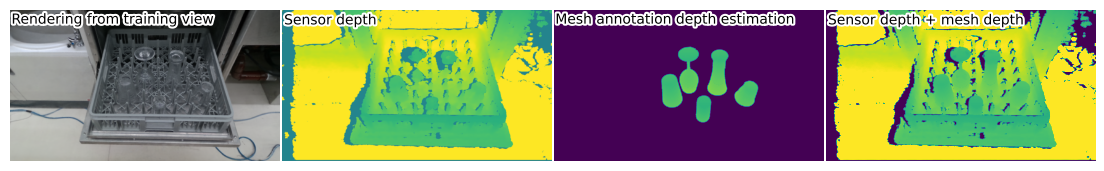
Dishwasher30k evaluation
We took a U-Net from a previous study that used a weakly supervised training procedure and trained it on a similar dataset using ground truth depth annotations that were generated using NeuralLabeling.
| Training regime | Modality | RMSE (m) ↓ | MAE (m) ↓ | Rel ↓ | 1.05 ↑ | 1.10 ↑ | 1.25 ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint Bilateral Filter | RGBD2Depth | 0.067 | 0.048 | 0.083 | 0.477 | 0.688 | 0.950 |
| ClearGrasp | RGBD2Depth | 0.090 | 0.057 | 0.120 | 0.404 | 0.555 | 0.840 |
| Cyclic adversarial | RGBD2RGBD | 0.061 | 0.040 | 0.072 | 0.528 | 0.767 | 0.940 |
| Cyclic adversarial | Depth2Depth | 0.058 | 0.035 | 0.061 | 0.589 | 0.861 | 0.954 |
| Dishwasher30k supervised | RGBD2Depth | 0.037 | 0.023 | 0.039 | 0.725 | 0.880 | 0.959 |
| Dishwasher30k supervised | Depth2Depth | 0.043 | 0.021 | 0.038 | 0.800 | 0.895 | 0.955 |
| Dishwasher30k supervised | RGB2Depth | 0.045 | 0.028 | 0.049 | 0.676 | 0.861 | 0.948 |
Sample
We generate supervised training data by aligning object models with transparent object NeRF scenes and combining sensor depth with object depth.
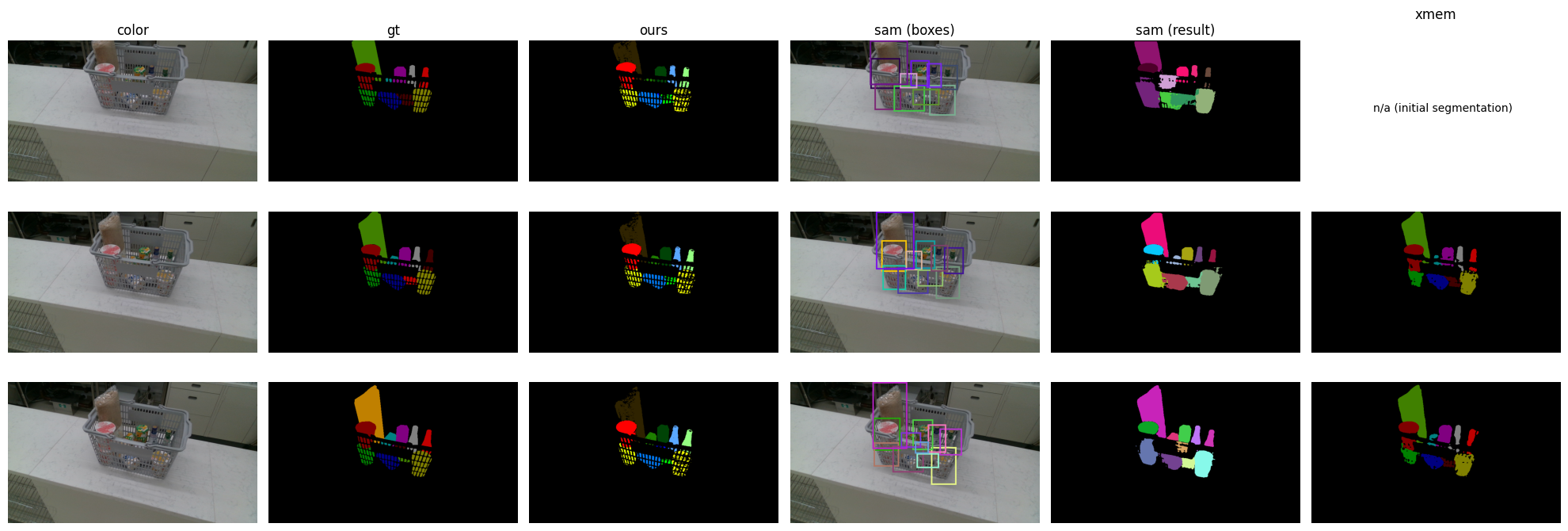
Segmentation evaluation
We compare segmentation quality using NeuralLabeling to segmentation quality using Segment Anything (SAM) and XMem in a scenario with heavy occlusions.
For SAM we manually annotate the scene using 2D bounding-boxes to indicate the objects to segment, for XMem we use the initial ground truth (gt) segmentation mask as input.
NeuralLabeling mostly performs comparably to XMem, while outperforming SAM.
NeuralLabeling can generate NeRF2Mesh occlusions, but NeRF depth estimates for transparent surfaces are noisy, causing some areas (e.g. towel) to have a poor segmentation quality.
NeuralLabeling can however create high quality segmentation masks for complex fence patterns.